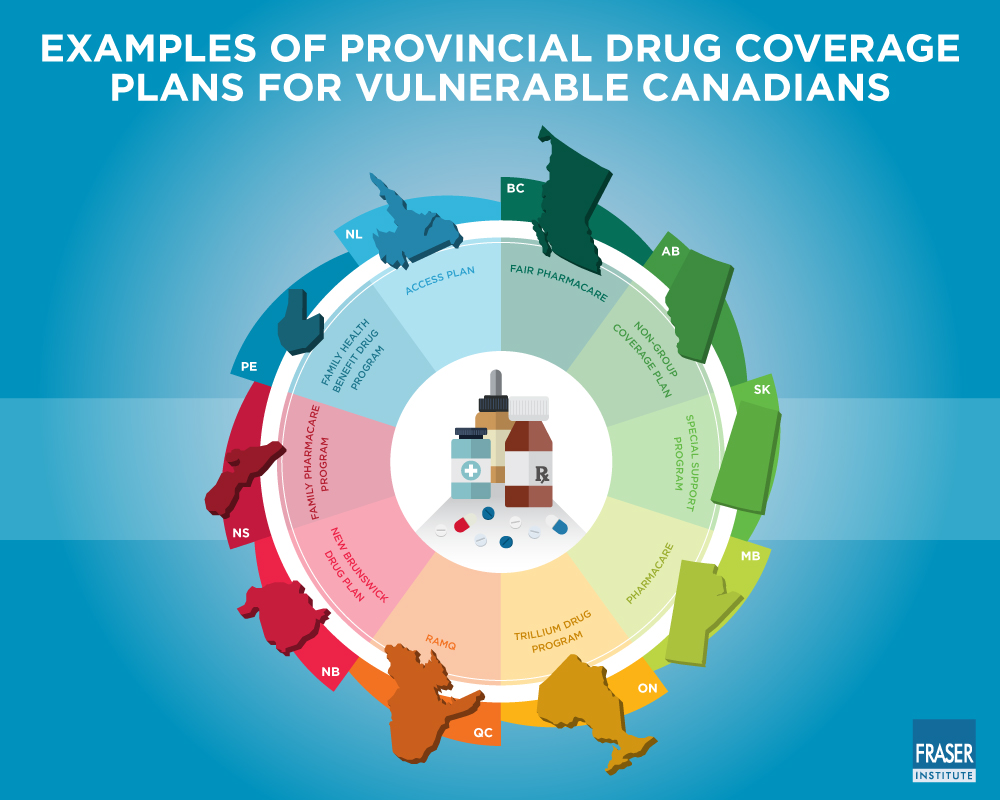
Explore the Public Pharmacare programs available in your province or territory. British Columbia, for instance, offers PharmaCare, a plan covering a significant portion of prescription drug costs for eligible residents, based on income and needs. Alberta’s coverage is more targeted, focusing on specific high-cost medications and vulnerable populations. Understanding these variations is key to accessing affordable healthcare.
Consider supplemental private plans to bridge gaps in public coverage. Many employers offer drug insurance as part of employee benefits packages, often reducing out-of-pocket expenses. Independent plans are also available, providing additional coverage for medications not included in your provincial plan. Compare plans carefully, focusing on the specific drugs you need and their associated costs.
Remember to check for eligibility requirements and income thresholds for both public and private plans. Provinces utilize different criteria for determining financial assistance, with application processes varying in complexity. Don’t hesitate to contact your provincial health authority or a private insurer directly for personalized guidance on enrolment and coverage specifics. This proactive approach ensures you receive the medication you need at the most affordable price.
Take action: Review your province’s specific drug plan details online. Many provinces provide user-friendly websites outlining program benefits, eligibility criteria, and application forms. This allows you to quickly identify and access the financial assistance available to you.
- Canadian Drug Plans: A Comprehensive Guide
- Private Drug Insurance Plans
- Understanding Your Costs
- Finding Affordable Medications
- Additional Resources
- Public Drug Plans: Provincial and Territorial Variations
- Key Differences in Coverage
- Navigating Provincial Plans
- Private Drug Insurance: Understanding Your Options
- Comparing Plans: Key Factors
- Finding the Right Fit
- Eligibility and Enrollment: Navigating the Application Process
- Prescription Drug Costs: Managing Your Expenses
- Commonly Prescribed Drugs and Coverage: What’s Included?
- Finding Assistance and Resources: Support for Medication Access
Canadian Drug Plans: A Comprehensive Guide
Start by determining your eligibility for provincial or territorial drug plans. These publicly funded programs offer coverage based on your age, income, and health status. Eligibility requirements vary by province; check your provincial government’s website for details. For example, Ontario’s OHIP+ covers residents under 25, or those 65 and over. British Columbia offers the PharmaCare program, with assistance based on income and medication costs.
Private Drug Insurance Plans
Many employers offer private drug insurance as part of employee benefits packages. These plans often cover a broader range of medications and offer lower out-of-pocket costs compared to using only public plans. Review your employer’s benefits plan carefully to understand your coverage. Negotiating better drug coverage is sometimes possible during contract renewal.
Understanding Your Costs
Familiarize yourself with the terms “deductible,” “co-payment,” and “co-insurance.” These terms describe your share of medication costs. Deductibles are the amount you pay before insurance coverage begins. Co-payments are a fixed amount you pay per prescription. Co-insurance represents the percentage of the cost you are responsible for after meeting the deductible. Drug costs can vary widely, so comparing prices between pharmacies is beneficial.
Finding Affordable Medications
Generic drugs are often significantly cheaper than brand-name medications while providing the same active ingredients. Ask your pharmacist about generic alternatives. Government-sponsored drug programs frequently have formulary lists, specifying approved drugs covered at lower costs. Check these lists to find the most affordable option within your coverage.
Additional Resources
Many non-profit organizations provide assistance to individuals struggling to afford prescription medications. Several patient assistance programs offer financial aid. Your local pharmacist can guide you towards relevant resources in your area.
Public Drug Plans: Provincial and Territorial Variations
Canada lacks a national pharmacare program, resulting in significant differences across provinces and territories. Understanding these variations is crucial for accessing the best coverage.
Key Differences in Coverage
- Eligibility: Eligibility criteria vary. Some provinces prioritize seniors and low-income individuals, while others offer broader coverage. Check your province’s specific guidelines.
- Drug Lists: Each province maintains its own formulary – a list of covered medications. These lists differ, meaning a drug covered in one province might not be in another. Consult your province’s formulary for details.
- Co-payments: Cost-sharing requirements vary widely. Some provinces have higher co-pays than others, impacting out-of-pocket expenses. Compare provincial co-payment schemes before making decisions.
- Income-Based Programs: Several provinces offer income-based programs reducing co-pays for low-income residents. Eligibility requirements change, so regularly review your province’s income assistance programs.
Navigating Provincial Plans
- Identify your province’s health authority website: This is your primary resource for accurate and up-to-date information.
- Review the formulary: Confirm if your needed medications are covered.
- Assess your eligibility: Determine if you meet your province’s criteria.
- Understand co-payment structures: Calculate your potential out-of-pocket costs.
- Explore supplementary programs: Investigate available income-based assistance or private supplemental insurance options.
Provincial drug plans are complex. Directly contacting your provincial health authority or a qualified healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance.
Private Drug Insurance: Understanding Your Options
Consider your needs carefully before choosing a plan. Many private insurers offer various coverage levels, impacting your out-of-pocket costs. Compare plans based on your prescription drug usage and anticipated expenses. Factors like premium costs, deductible amounts, and co-payments significantly influence your total cost. Some plans cover specific medications, while others offer broader coverage. Check if your preferred medications are covered and what your cost-sharing will be.
Comparing Plans: Key Factors
Analyze premium costs against the level of coverage. A higher premium might mean lower out-of-pocket expenses. Conversely, a lower premium may lead to higher costs when you need medication. Look at the formulary–a list of covered drugs–to ensure your necessary prescriptions are included. Understand the process for appealing coverage decisions if a drug isn’t initially approved. Review the plan’s coverage details for pre-authorization requirements and any limitations on quantities. Investigate the insurer’s reputation and customer service ratings. Choose a plan that suits your budget and healthcare needs.
Finding the Right Fit
Check your employer’s benefits package – many offer group rates with private insurers. Compare options directly with insurers or use online comparison tools to see plans side-by-side. Speak to a benefits advisor or pharmacist for personalized guidance. Don’t hesitate to ask questions and clarify any confusing aspects of policy details. Remember, choosing the right private drug plan can significantly impact your healthcare costs.
Eligibility and Enrollment: Navigating the Application Process
Check your provincial or territorial health plan website for specific eligibility criteria. Age, residency, and income often play a role. Some plans cover only seniors or low-income individuals.
Gather necessary documents. This usually includes proof of residency, income statements, and possibly a health card. Keep copies of everything for your records.
Complete the application form accurately and thoroughly. Missing information delays processing. Double-check all details before submitting.
Submit your application. Many provinces offer online application portals; others require paper applications. Follow the instructions precisely. Provincial websites usually provide contact information for assistance with the application process.
Expect a processing time. Processing times vary by province and application volume. Check the status of your application online if possible.
Understand your coverage. Once approved, review your benefits carefully. Pay attention to co-payments, deductibles, and drug formularies.
Contact your provincial or territorial health plan if you have questions or require clarification. Their phone numbers and email addresses are readily available on their respective websites.
Note: Eligibility rules and application procedures differ significantly between provinces and territories.
Remember to confirm the most up-to-date information directly from your province’s official health insurance website.
Prescription Drug Costs: Managing Your Expenses
Explore your provincial drug plan coverage thoroughly. Understanding your benefits–including co-pays, formularies, and coverage limitations–is crucial for budgeting.
Consider generic medications. They often cost significantly less than brand-name drugs and offer the same active ingredients.
- Generic drugs can reduce your expenses by 30-80% or more.
- Discuss generic options with your pharmacist or doctor.
Negotiate prices. Ask your pharmacist about potential discounts or programs. Many pharmacies offer savings cards and loyalty programs.
- Check for manufacturer coupons or patient assistance programs directly.
- Explore online resources for medication price comparisons.
Use a prescription drug discount card. These cards can provide savings even if you have insurance. Compare various cards to find the best deal for your specific needs.
Maintain open communication with your doctor. Discuss your financial constraints. They might suggest alternative medications or treatment plans that are more cost-effective.
Explore support programs. Many charities and non-profit organizations offer assistance with prescription drug costs. Research the options available in your province or territory.
- Eligibility requirements vary, so verify your suitability for each program.
- Don’t hesitate to seek assistance if you need it.
Pay attention to refill schedules. Manage your medications effectively to avoid unnecessary costs associated with early refills or wasted medication.
Commonly Prescribed Drugs and Coverage: What’s Included?
Check your provincial or territorial plan for specifics, but generally, most plans cover many common medications. This includes drugs for managing chronic conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure.
For example, many plans cover insulin for diabetes management, various blood pressure medications like ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers, and statins to lower cholesterol. Coverage for mental health medications, such as antidepressants and anti-anxiety drugs, is also frequently included.
However, coverage can vary based on your specific plan and the drug’s generic status. Generic medications are generally cheaper and often fully covered. Brand-name drugs may have partial coverage or require pre-authorization.
| Drug Category | Example Drugs | Typical Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes Medications | Insulin (various types), Metformin | Generally good coverage for generics; brand-name coverage may vary |
| High Blood Pressure Medications | Lisinopril, Metoprolol | Generally good coverage for generics; brand-name coverage may vary |
| Cholesterol-Lowering Medications | Atorvastatin, Simvastatin | Generally good coverage for generics; brand-name coverage may vary |
| Mental Health Medications | Sertraline, Fluoxetine | Coverage varies widely depending on the plan and specific drug |
Always confirm coverage with your specific drug plan provider before filling prescriptions. They can provide a detailed list of covered medications and explain any cost-sharing requirements. This information usually updates regularly, so it’s crucial to check frequently.
For drugs not covered or with limited coverage, consider exploring options like patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical companies. Many offer financial help to eligible patients.
Finding Assistance and Resources: Support for Medication Access
Check your eligibility for provincial or territorial drug plans. These plans offer coverage based on income and other factors. Contact your provincial health ministry directly for details and application information.
Explore the Trillium Drug Program in Ontario. This program assists residents with high drug costs, regardless of income. The application process is available online, and requirements are clearly outlined on their website.
Investigate the various non-profit organizations offering medication assistance. Many charities provide financial aid or connect individuals with discounted prescription programs. Research local and national organizations; several specialize in specific health conditions.
Contact your pharmacist. Pharmacists often have knowledge of patient assistance programs offered by drug manufacturers. They can advise you on available options and help with the application process. Don’t hesitate to ask!
Consider the potential for government subsidies. Federal and provincial initiatives can reduce drug costs for seniors and low-income individuals. Look into programs like the Canada Pension Plan (CPP) and Guaranteed Income Supplement (GIS) for further benefits.
Use online resources. Several websites provide comprehensive databases of patient assistance programs and drug discounts. Consult these sites for updated information and search for relevant programs specific to your medications and needs.
Remember: Eligibility criteria and application processes vary. Carefully review the specific requirements of each program.
Proactive engagement with available resources is key to accessing affordable medications. Don’t delay seeking assistance.